A1
What is an isolation transformer?
The isolation referred to in an isolation transformer means that the secondary and primary windings are separated by insulation to electrically isolate them, and they maintain a safe distance from each other. The isolation isolates the currents of the primary and secondary coils. The function of an isolation transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction as well. Since the secondary side is not grounded, there is no potential difference between any wire on the secondary side and the ground, which makes it safe to use. An isolation transformer is often used as a maintenance power supply.
In addition, not all isolation transformers refer to a 1:1 transformer. Control transformers and power supplies for electronical equipment are also isolation transformers, such as amplifiers, radios, oscilloscopes, and lathe machine tool control transformers. Isolation transformers are widely used, which are also used in air conditioners.
In addition, not all isolation transformers refer to a 1:1 transformer. Control transformers and power supplies for electronical equipment are also isolation transformers, such as amplifiers, radios, oscilloscopes, and lathe machine tool control transformers. Isolation transformers are widely used, which are also used in air conditioners.
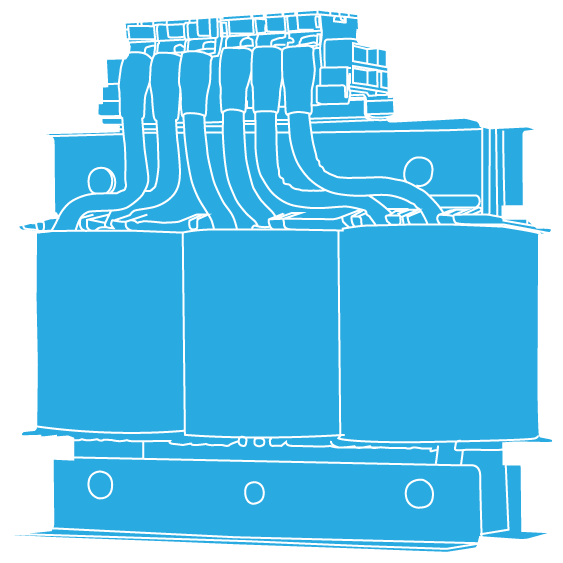
A2
What is an autotransformer?
An autotransformer is a special case, in which one coil becomes part of another coil. Autotransformers are also often used for starting motors. An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding, and portions of the same winding act as both the primary winding and secondary winding sides of the transformer.
For an autotransformer, portion of the winding is shared by both the high-voltage side and the low-voltage side. The other part only belongs to the high-voltage side. According to the structure, it can also be subdivided into two types: adjustable pressure type and fixed type. Auto-coupling means electromagnetic coupling. Ordinary transformers transfer energy through the electromagnetic coupling of the primary and secondary coils, in which there is no direct electrical connection between the primary and secondary sides. However, the primary and secondary sides of the autotransformer have direct electrical connections, and the low-voltage coils are part of the high voltage coils. An autotransformer works on the same principle as that of an ordinary transformer, except that its primary coil is its secondary coil. In a general transformer, the primary side coil generates voltage on the secondary side through electromagnetic induction. The autotransformer affects itself.
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. Compared with ordinary transformers of the same capacity, autotransformers are not only smaller in size, but also more efficient. In addition, the larger the capacity of the transformer is, the higher the voltage is, and this advantage becomes more outstanding. Therefore, with the development of power systems, an increase of the voltage level and the increasing transmission capacity, autotransformers have been widely used because of their high capacity, low loss, and low cost.
For an autotransformer, portion of the winding is shared by both the high-voltage side and the low-voltage side. The other part only belongs to the high-voltage side. According to the structure, it can also be subdivided into two types: adjustable pressure type and fixed type. Auto-coupling means electromagnetic coupling. Ordinary transformers transfer energy through the electromagnetic coupling of the primary and secondary coils, in which there is no direct electrical connection between the primary and secondary sides. However, the primary and secondary sides of the autotransformer have direct electrical connections, and the low-voltage coils are part of the high voltage coils. An autotransformer works on the same principle as that of an ordinary transformer, except that its primary coil is its secondary coil. In a general transformer, the primary side coil generates voltage on the secondary side through electromagnetic induction. The autotransformer affects itself.
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding. Compared with ordinary transformers of the same capacity, autotransformers are not only smaller in size, but also more efficient. In addition, the larger the capacity of the transformer is, the higher the voltage is, and this advantage becomes more outstanding. Therefore, with the development of power systems, an increase of the voltage level and the increasing transmission capacity, autotransformers have been widely used because of their high capacity, low loss, and low cost.
A3
Advantages of Toroidal Transformers
1.High efficiency, no air gap in the iron core, the lamination factor may be more than 95%, and it is possible to have higher than 95% efficiency.
2.Small size and light weight, and the appearance size can be designed to meet the requirements.
3.The magnetic interference is small, and the magnetic leakage is small as well, with a small part of electromagnetic radiation, it can be used in highly sensitive electronic devices without additional shielding.
4.Small vibrating sound, and there is no air gap in the iron core to reduce the induced vibration noise in the iron core.
5.Small iron loss, the core temperature rise is low, and the windings dissipate heat well on the lower-temperature core, which results in a low temperature rise of the transformer.
6.Easy to quickly install in and remove from electronical equipment.
A4
What is a transformer?
The transformer is a static device, which produces a voltage difference between the primary side and the secondary side through the combination of changes in the coil windings and the magnetic field of the iron core, enabling the user to select the required voltage for the use of equipment. Due to the output of various countries, the transmission voltages are all different; thus, the transformer becomes the best bridge between the power transmission/distribution and the device end.

A5
What are the types of transformers?
Transformers can be divided into two categories: dry-type transformers and oil-type transformers. There are also die-cast transformers for you to choose depending on the situation.
Generally, dry-type transformers are commonly used indoors. Oil-immersed transformers are more commonly used for outdoor power transmission and distribution because they have a shell, and the transformer should be immersed in insulating oil. Certainly, all forms of transformer can be used so long as environmental requirements permit. Dry-type transformers play an indispensable role in many machines and equipment because of their small size and large voltage changes.
Generally, dry-type transformers are commonly used indoors. Oil-immersed transformers are more commonly used for outdoor power transmission and distribution because they have a shell, and the transformer should be immersed in insulating oil. Certainly, all forms of transformer can be used so long as environmental requirements permit. Dry-type transformers play an indispensable role in many machines and equipment because of their small size and large voltage changes.
A6
What are the tests for transformers?
In addition to basic voltage test, transformers also include transformer ratio test, copper and iron loss test, temperature rise test, withstand voltage test, insulation resistance test, ground continuity test, high-frequency test, inrush current testing, and noise test.


 Knowledge Base
Knowledge Base


